An Insight into Faraday cage's Applications and Working Mechanisms
What is a faraday cage?
What are the best Faraday cages?
Discover the scientific brilliance of Faraday cages shielding equipment and individuals from electromagnetic radiation
In the realm of electromagnetic fields and radiofrequency interference, Faraday cages stand as remarkable inventions that have revolutionized various scientific and technological domains. Originally conceived by the renowned physicist Michael Faraday in the early 19th century, these cages provide an effective means of shielding sensitive equipment people, and spaces from electromagnetic radiation. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of Faraday cages, exploring their applications and uncovering the underlying principles that make them so effective.
What is a faraday cage?
Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who invented them in 1836.
Faraday cages block electromagnetic fields (EMF).
They are made out of metal and shield all around, like a cage.

What are EMFs?
What are Electro Magnetic Fields?
-
Electric fields.
-
Magnetic fields.
Electric and magnetic fields
EMFs are both electric fields and magnetic fields from HF (High Frequenzies) and LF (Low Frequenzies).
Radio Frequencies (RF). These are HF, High Frequenzy. Both microwaves and radio waves are radio frequencies. In daily term, we call it mobile phone radiation from WiFi, mobile phones, masts and antennas, Bluetooth, smart meters, and wireless devices.

Electromagnetic shielding
Faraday cages block EMFs.
Modern faraday cages are made out of fine masked metal mesh or silver coated canopy net.
You can see throgh the mesh or the tiny net holes.
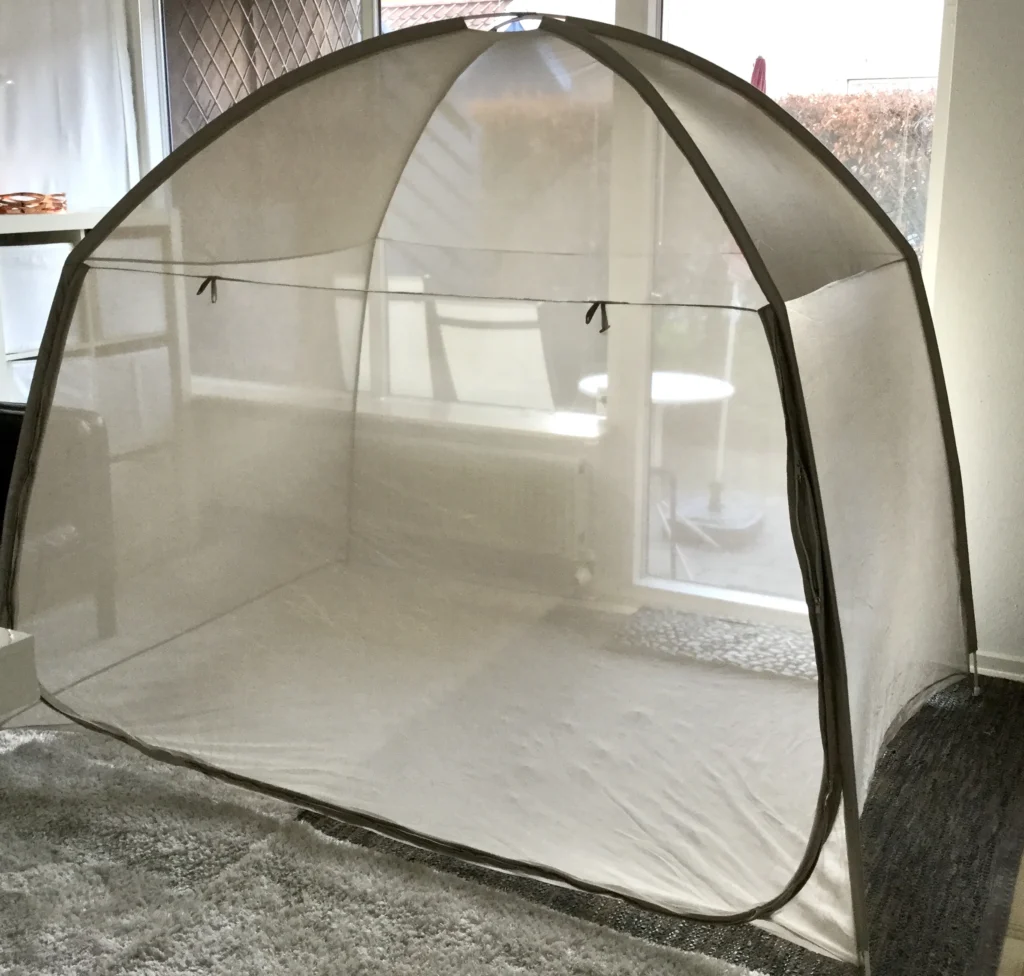
Faraday cages have metal all around, including on the ground.

The door must be closed after entering the Faraday cage.
On this picture, both the beige fabric and the blue carpet is made out of metal.
Faraday cages both shield electric and magnetic fields
Radio frequencies have both electric and magnetic fields.
This means that Faraday cages both shield electric and magnetic fields.

How does a faraday cage work?
The Faraday Cage stops electricity and electromagnetic frequencies from entering the cage, affectivly insulating any object inside from electricity.
Faraday Cages Explained [IN UNDER 3 MINUTES]
Faraday cages and electrostatic shielding
Electrostatic shielding.
Please notice that a faraday cage that must shield against RF and other wireless radiation must have much smaller holes than the one in this video. It´s because the EMF waves from RF are small enough to enter a faraday cage with big holes, so it needs tiny holes.
Professor Krishna Rajagopal explains Faraday Cages and why it’s not such a bad thing if you’re in a lightning storm as long as you’re inside a car.
Read more about faraday cages here
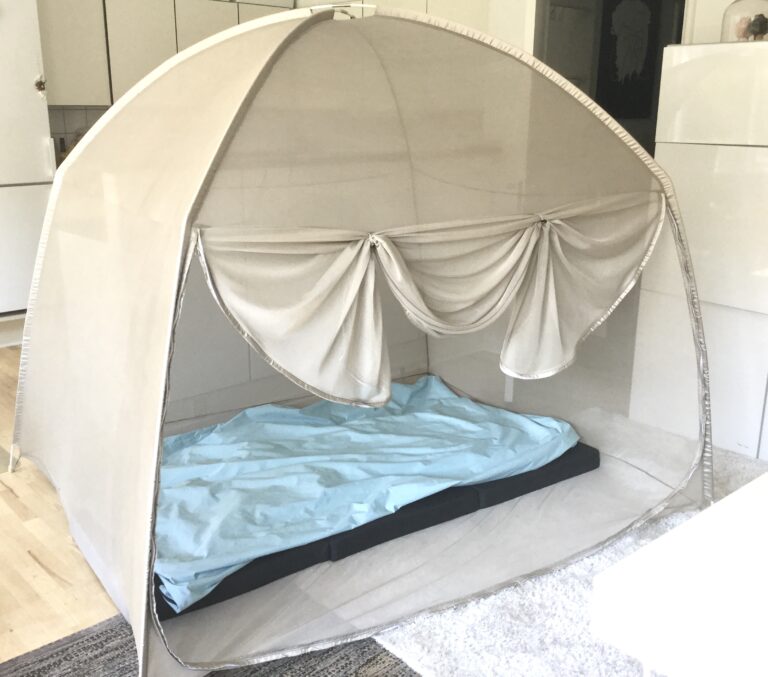

Are you looking for your own faraday cage?
Ehsshield offers the highest protection against wireless radiation in the world of faraday cages.
Faraday cages in silver net.
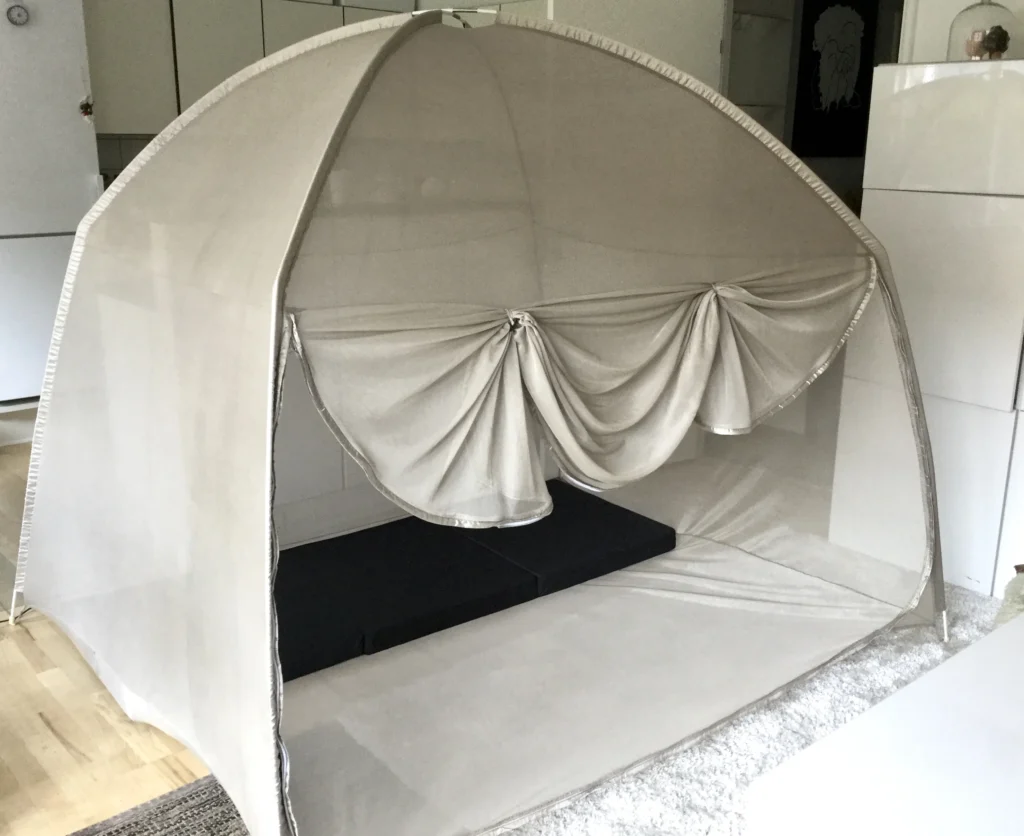

Our faraday cages for sleeping are tested up to 10 GHz.
They are 5G tested.
Read more here!
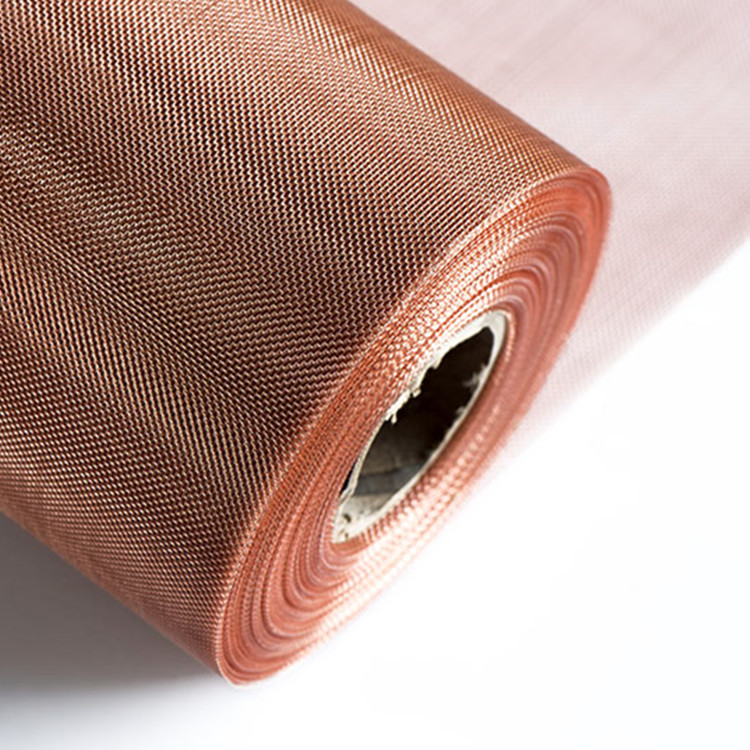

Faraday cages in metal made with tiny mesh holes.
Copper, bronze, stainless steel, and brass.
Faraday cages and sleeping
The highest shielding in the world of faraday cages
We recommend Faraday cages in silver net for modern homes to shield against wireless radiation
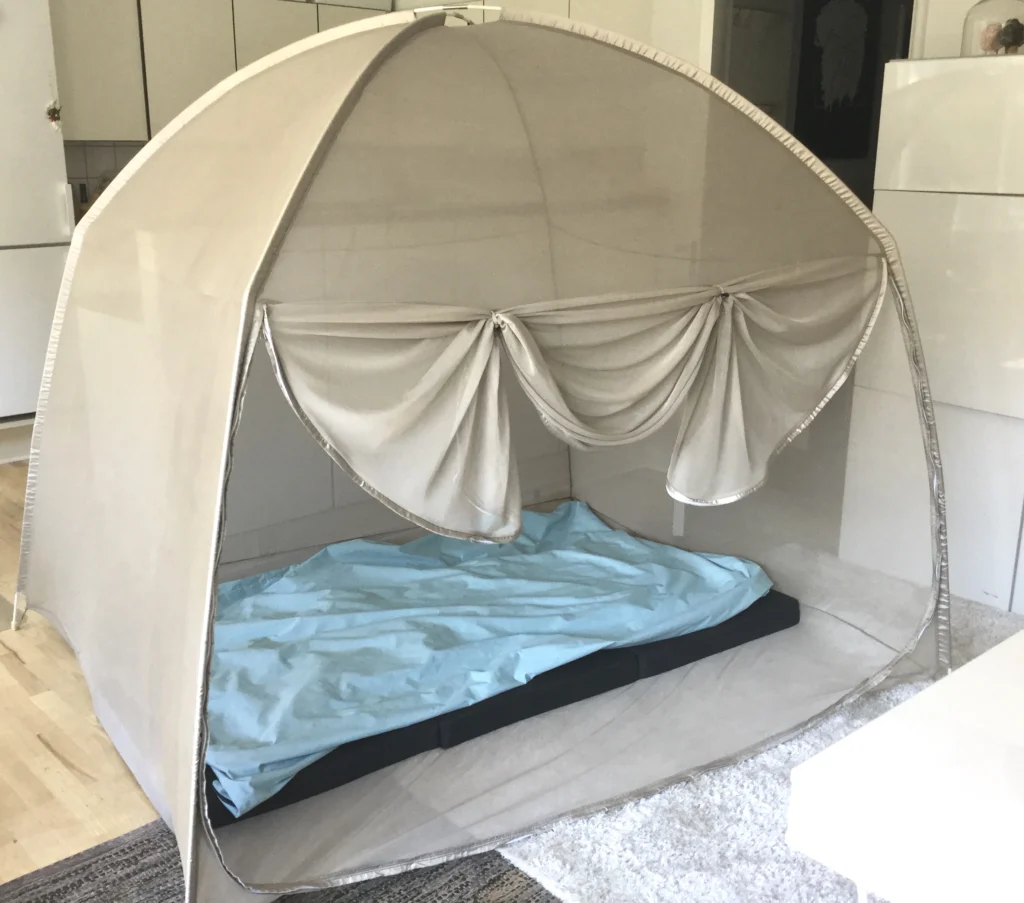

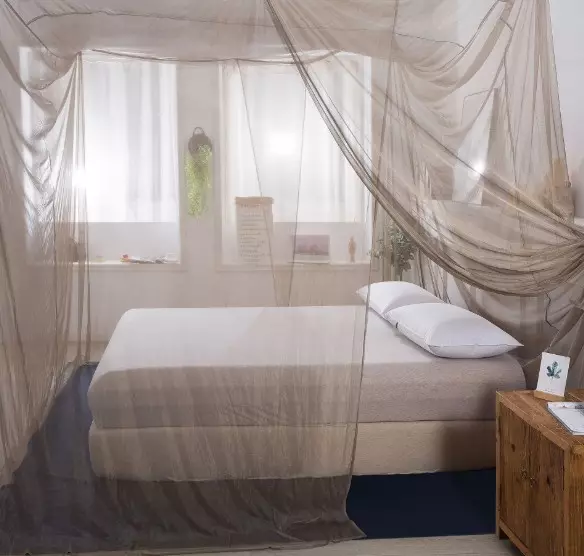
Here you can see a Faraday cage made out of silver canopy net.
Faraday cages made out of net
Faraday cages made out of Silver canopy net are ideal for sleeping and for modern homes.
They have so tiny holes that the holes are not measured in mesh. The holes are not square either. They are tiny tiny.
The protection is measured in dB. Please be aware that the shielding varies depending at what GHz the radio frequenzy radiation is.
The best possible protection for Faraday Cages made out of silver net is 51 dB and is offered by Ehsshield.
More about Faraday cages and about how they work
Applications of Faraday Cages: Faraday cages find wide-ranging applications across multiple industries due to their ability to attenuate or block electromagnetic radiation. Here are some notable applications:
-
Electronics and Telecommunications: Faraday cages are extensively utilized in electronic and telecommunications industries to shield sensitive electronic components and devices. They safeguard against electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can disrupt or damage the proper functioning of delicate circuits and systems.
-
Scientific Research and Testing: In scientific laboratories and testing facilities, Faraday cages play a crucial role in creating controlled electromagnetic environments. They prevent external interference during sensitive experiments, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements in fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology.
-
Data Security: Faraday cages are employed in data centers and secure facilities to shield electronic equipment and storage media from external electromagnetic signals. This ensures protection against unauthorized access, data theft, and interception of sensitive information.
-
Medical and Healthcare: In the medical field, Faraday cages are utilized to safeguard sensitive equipment like MRI machines, EEG devices, and other medical imaging systems. These cages isolate the equipment from external electromagnetic radiation, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic procedures.
-
Defense and Military: Faraday cages have critical applications in defense and military domains. They protect electronic systems, communication devices, and sensitive equipment from electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attacks and interference, enhancing their operational resilience.
-
Faraday Cages for Homes: Faraday cages have expanded beyond industrial use and are now utilized in people’s homes to shield against electromagnetic radiation. As electronic devices and wireless technologies become more prevalent, concerns about potential health risks have grown. Incorporating Faraday cages into home design provides electromagnetic-safe spaces, reducing exposure to electromagnetic fields and mitigating interference from household devices and the electromagnetic environment outside.
-
Personal Shielding: Personal shielding solutions, such as EMF protection clothing, utilize the principles of Faraday cages. This approach recognizes the needs and concerns of individuals who prioritize or require reduced exposure to electromagnetic radiation. The shielding can be all from wearable canopies on an umbrella, to headnets, to shielding clothing made out of silver fiber materials, The shielding clothes offer a layer of protection, reducing the intensity of electromagnetic fields reaching the body. Personal shielding empowers individuals to cope with or manage the electromagnetic environment with modern technologies.
How Faraday Cages Work:
The metal cages are constructed using conductive materials, typically metals like copper or aluminum are effective in shielding against EMFs.
When RF hits the metal on the Faraday cage it gets thrown back and cannot enter.
When an external electromagnetic field hits the Faraday cage, the conductive material leads the electromagnetic field to the ground. This blocks out the field and the passage of the electromagnetic radiation. Both LF and HF (RF) carry magnetic fields. RF are also radio waves or microwaves and the radiation waves hit the metal and are being blocked . The Faraday cage must have smaller holes than the RF waves or it must have no holes at all. The size of the metal mesh holes are of importance when it comes to shielding against RF (HF).
The effectiveness of a Faraday cage depends on several factors, including the thickness and conductivity of the enclosing material. It is crucial to ensure a continuous conductive enclosure with no gaps or seams that could allow electromagnetic waves to penetrate.
Additionally, Faraday cages must be properly grounded to facilitate the dissipation of any accumulated electric charge. This grounding prevents the buildup of static electricity within the cage, maintaining its shielding effectiveness. Often it’s enough simply to touch the ground for grounding effect. The Faraday cage itself must touch the ground. In some cases, the Faraday cage can be connected to additional metal connected to the ground. Because metai is conductive, itś a good idea not to connect the Faraday cage to an electrical source like a socklet simply because LF can go both ways.
Rememeber, the Faraday cage must be shieldes with metql all around like a box and it must touch the ground.
Conclusion
Faraday cages have become essential tools in shielding sensitive equipment, people, and spaces from electromagnetic radiation, addressing the dual nature of modern technology.
Ongoing research and innovations in materials and design enhance the effectiveness of Faraday cages, ensuring a secure environment for critical operations and equipment. These cages bridge the gap between the positive and negative aspects of modern technology. In an interconnected world, Faraday cages play a pivotal role in providing reliable protection, safeguarding both the benefits of technology and individual well-being.
Sign up for our newsletter
“
Get the latest news about Faraday Cages here
Faraday Cage
Subscribe to our newsletter!

